From Deep Additive Kernel Learning to Last-Layer Bayesian Neural Networks via Induced Prior Approximation
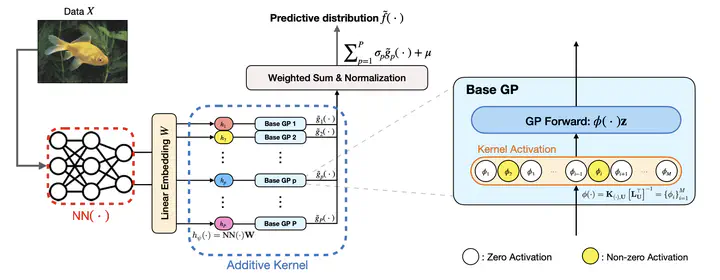 Image credit: Wenyuan Zhao
Image credit: Wenyuan ZhaoAbstract
With the strengths of both deep learning and kernel methods like Gaussian Processes (GPs), Deep Kernel Learning (DKL) has gained considerable attention in recent years. From the computational perspective, however, DKL becomes challenging when the input dimension of the last-layer GP is high. To address this challenge, we propose the Deep Additive Kernel (DAK) model, which incorporates i) an additive structure for the last-layer GP; and ii) induced prior approximation for each GP component. This naturally leads to a last-layer Bayesian neural network (BNN) architecture. The proposed method enjoys the interpretability of DKL as well as the computational advantages of BNN. Empirical results show that the proposed approach outperforms state-of-the-art DKL methods in both regression and classification tasks.
Comments